A) the rate of decay of a radioactive source
B) the ability of a beam of gamma ray photons to produce ions in a target
C) the energy delivered by radiation to a target
D) the biological effect of radiation
E) none of the above
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fly caught in amber is thought to be 3 million years old. Why would it not be useful to confirm its age using radiocarbon dating?
A) The fly contains no carbon.
B) The fly is too small to contain a measurable amount of carbon.
C) The fly is too old to contain a measureable amount of carbon-14.
D) The carbon-14 doesn't begin to decay until the fly is removed from the amber.
E) Radiocarbon dating is too inaccurate to be useful.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mass density of an atomic nucleus:
A) is about 1015 kg/m3
B) is about 1012 kg/m3
C) increases with increasing nuclear mass
D) increases with decreasing nuclear radius
E) is roughly constant independent of atomic number
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nucleus with mass number A and atomic number Z undergoes + decay. The mass number and atomic number, respectively, of the daughter nucleus are:
A) A - 1, Z - 1
B) A - 1, Z + 1
C) A + 1, Z - 1
D) A, Z + 1
E) A, Z - 1
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gray is the correct unit to use in reporting the measurement of:
A) the rate of decay of a radioactive source
B) the ability of a beam of gamma ray photons to produce ions in a target
C) the energy delivered by radiation to a target
D) the biological effect of radiation
E) none of the above
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bombardment of 28Si (Z = 14) with alpha particles may produce:
A) a proton and 31P (Z = 15)
B) hydrogen and 32S (Z = 16)
C) a deuteron and 27Al (Z = 13)
D) helium and 31P (Z = 15)
E) 35Cl (Z = 17)
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A femtometer is:
A) larger than 10-9 m
B) 10-9 m
C) 10-12 m
D) 10-15 m
E) 10-18 m
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two protons are about 10-10 m apart. Their relative motion is chiefly determined by:
A) gravitational forces
B) electrical forces
C) nuclear forces
D) magnetic forces
E) torque due to electric dipole moments
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Rutherford scattering experiment showed that:
A) light has both particle-like and wavelike properties
B) atoms are electrically neutral
C) the positive and negative charges in the atom are uniformly distributed throughout its volume
D) the wavelength of scattered light depends on the scattering angle
E) the atom consists of a very tiny, massive, positively charged nucleus surrounded by almost empty space
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which expression correctly describes the radioactive decay of a substance whose half-life is T?
A) N(t) = N0e-(t ln2) /T
B) N(t) = N0e-t/T
C) N(t) = N0e-tT
D) N(t) = N0e-tT ln2
E) N(t) = N0e-t/T ln2
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nucleus with mass number A and atomic number Z emits an alpha particle. The mass number and atomic number, respectively, of the daughter nucleus are:
A) A, Z -2
B) A - 2, Z - 2
C) A - 2, Z
D) A - 4, Z
E) A - 4, Z - 2
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stable nuclei generally:
A) have a greater number of protons than neutrons
B) have low mass numbers
C) have high mass numbers
D) are beta emitters
E) none of the above
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two protons are separated by 10-16 m. The nuclear (N) , electrostatic (E) , and gravitational (G) forces between these protons when written in order of increasing strength are:
A) N, E, G
B) N, G, E
C) G, E, N
D) G, N, E
E) E, G, N
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the following collections of particles according to the total binding energy of all the particles in each collection, least to greatest. 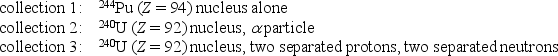
A) 1,2,3
B) 3,2,1
C) 2,1,3
D) 1,3,2
E) 2,3,1
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The half-life of radium is about 1600 years. If a rock initially contains 1 g of radium, the amount left after 8000 years will be about:
A) 200 mg
B) 63 mg
C) 31 mg
D) 16 mg
E) less than 1 mg
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aluminum has atomic number 13, helium has atomic number 2, and silicon has atomic number 14. In the nuclear reaction 27Al + 4He 30Si + ( ) the missing particle is:
A) an particle
B) a positron
C) an electron
D) a proton
E) a neutron
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Beta particles from various radioactive sources all have:
A) the same mass
B) the same speed
C) the same charge
D) the same deflection
E) the same energy in a magnetic field
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Radioactive polonium, 214Po (Z = 84) , decays by alpha emission to:
A) 214Po (Z = 84)
B) 210Pb (Z = 82)
C) 214At (Z = 85)
D) 218Po (Z = 84)
E) 210Bi (Z = 83)
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The atomic number of an element is:
A) the whole number nearest to its mass
B) the number of protons in its nucleus
C) the nearest whole number of hydrogen atoms having the same mass as a single atom of the given element
D) the number of neutrons in its nucleus
E) its order of discovery
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A large collection of nuclei are undergoing alpha decay. The rate of decay at any instant is proportional to:
A) the number of undecayed nuclei present at that instant
B) the time since the decays started
C) the time remaining before all have decayed
D) the half-life of the decay
E) the average time between decays
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 68
Related Exams