A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
F) ![]()
G) BOC group
H) ![]()
I) ![]()
J) ![]()
K) ![]()
L) ![]()
M) Z group
O) C) and K)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following amino acids has a polar side chain?
A) isoleucine
B) valine
C) phenylalanine
D) threonine
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following amino acids is a secondary amine?
A) proline
B) glutamine
C) cysteine
D) aspargine
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Valylalanine and alanylvaline are constitutional isomers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following natural amino acids is an R-isomer?
A) cysteine
B) serine
C) valine
D) phenylalanine
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a definition of the isoelectric point of an amino acid?
A) The pH at which an amino acid has no net charge
B) The pH at which the -NH2 group is completely protonated
C) The melting point of an amino acid
D) The conductivity of a 1 M solution of an amino acid in water
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following amino acids has a basic side chain?
A) lysine
B) serine
C) leucine
D) tyrosine
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To what structural feature does the term "tertiary structure" refer?
A) the sequence of amino acids in proteins
B) the overall folding pattern of proteins
C) the aggregation of polypeptides
D) the conformation of local regions of polypeptides
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the isoelectric point of glutamic acid (pKa of -CO2H, 2.10; pKa of -CO2H, 4.07; pH of -NH2, 9.47) ?
A) 3.08
B) 5.67
C) 6.16
D) 17.28
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following dipeptides is L-Ser-L-Phe? 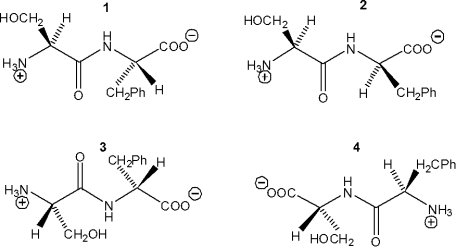
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 70 of 70
Related Exams