A) restrictive fiscal policy is an effective weapon against inflation.
B) expansionary fiscal policy will be a highly effective weapon for fighting a recessionary downturn
C) a budget surplus will cause the demand for loanable funds to decline, interest rates to rise, and aggregate demand to decrease.
D) budget deficits that lead to higher interest rates reduce private investment spending.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The paradox of excessive consumption argues that when households spend all they earn,
A) actual output and potential output will be in equilibrium.
B) the financial anxiety of families will be low.
C) the economy will achieve rapid, sustainable growth.
D) consumption can stagnate because families are in a poor position to deal with increases in debt and financial setbacks.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The crowding-out effect stresses that increased government borrowing to cover a budget deficit will cause
A) a higher interest rate and depreciation of the U.S. dollar.
B) a higher interest rate and appreciation of the U.S. dollar.
C) a lower interest rate and depreciation of the U.S. dollar.
D) a lower interest rate and appreciation of the U.S. dollar.
E) no change in the interest rate and depreciation of the U.S. dollar.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the crowding-out effect is strong, how will the potency of discretionary fiscal policy be affected?
A) It will make fiscal policy more potent.
B) It will make fiscal policy less potent.
C) The potency of fiscal policy will be unaffected.
D) The potency of expansionary fiscal policy will be reduced, but that of restrictive fiscal policy will be enhanced.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an argument for tax cuts rather than government spending as a way to promote recovery from a recession?
A) Tax cuts are better suited to direct resources into projects that consumers value more highly than the resources required for their production.
B) 100 percent of a tax cut will stimulate aggregate demand, but this will not be the case for an increase in government expenditures.
C) Tax cuts will encourage rent seeking; increases in government spending will not.
D) Tax cuts will change the structure of aggregate demand more than increases in government spending.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When government spending flows to areas where resources are already fully employed,
A) the additional spending will stimulate strong growth in those areas.
B) aggregate demand will place downward pressure on the general level of prices.
C) the coordination problem accompanying the composition of aggregate demand is likely to improve.
D) the coordination problem accompanying the composition of aggregate demand is likely to worsen.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If decreased government borrowing drives down real interest rates in the United States,
A) private investment will tend to decline.
B) the dollar will depreciate leading to an increase in net exports.
C) an inflow of capital will cause the dollar to depreciate.
D) All of the above are true.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is an area of continued disagreement among modern macroeconomists with regard to the use of fiscal policy?
A) Automatic stabilizers help reduce the fluctuations in aggregate demand and output.
B) It is difficult to time changes in discretionary fiscal policy in a manner that will promote stability.
C) Fiscal policy is much less potent than the early Keynesian view implied.
D) Budget deficits are a highly effective tool with which to combat a severe recession.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things being constant, countries with higher rates of saving
A) will have smaller GDPs than countries with lower rates of saving.
B) will have higher rates of investment, but slower growth.
C) will have higher rates of investment and growth.
D) will be operating at less than full employment and potential output.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is part of the synthesis view of fiscal policy?
A) Automatic stabilizers offset some of the fluctuations in aggregate demand without any government action.
B) Fiscal policy is much less potent than the early Keynesian view implied.
C) The effectiveness of discretionary fiscal policy as a stabilization tool is highly questionable given the difficulties in proper timing.
D) All of the above are correct.
E) None of the above is correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following most accurately indicates the political incentive to spend and/or tax?
A) Politicians will find tax increases more attractive than increases in government expenditures.
B) Voters will generally support higher taxes in order to eliminate budget deficits.
C) Politicians are rewarded for raising taxes and punished for providing programs that benefit their constituents.
D) Politicians are rewarded for providing programs that benefit their constituents and punished for raising taxes.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s) . Figure 12-1
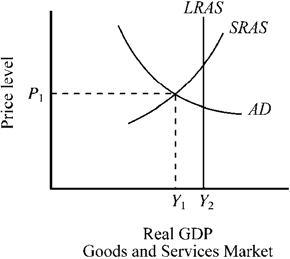 Refer to Figure 12-1. If the output of the economy is Y1, which of the following would a new classical economist be most likely to favor?
Refer to Figure 12-1. If the output of the economy is Y1, which of the following would a new classical economist be most likely to favor?
A) a reduction in government expenditures
B) a reduction in taxes
C) an increase in taxes
D) continuation of the current tax and expenditure policies
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spending programs that substantially alter the composition of aggregate demand will tend to
A) decrease the rate of unemployment.
B) increase the rate of unemployment.
C) promote a more rapid recovery.
D) reduce structural unemployment.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s) . Figure 12-2
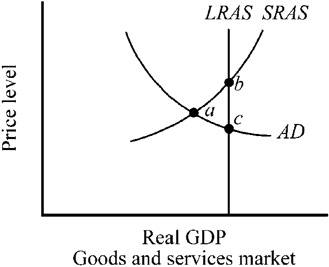 Refer to Figure 12-2. If an economy is operating in the short run at point a, Keynesian analysis indicates that expansionary fiscal policy will
Refer to Figure 12-2. If an economy is operating in the short run at point a, Keynesian analysis indicates that expansionary fiscal policy will
A) increase AD and move the economy toward point b.
B) increase AD and move the economy toward point c.
C) increase SRAS and move the economy toward point b.
D) decrease SRAS and move the economy toward point c.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During 1960-1980, those with the highest incomes confronted federal marginal tax rates between 70 and 90 percent. Since 1986, the highest federal income tax rate has been less than 40 percent. Since 1986, the share of the personal income tax collected from the top one-half of one percent of earners has been
A) substantially lower than during the 1960s and 1970s.
B) only slightly lower than during the 1960s and 1970s.
C) virtually the same as during the 1960s and 1970s.
D) higher than during the 1960s and 1970s.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
New classical economists stress that an increase in government expenditures financed by borrowing rather than taxes will
A) exert a strong expansionary impact on aggregate demand and real output.
B) affect the timing of taxes but not their magnitude.
C) lead to higher interest rates.
D) undermine confidence and reduce the level of private saving.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following most clearly states the "paradox of thrift"?
A) If households simultaneously attempt to increase their savings, the result may be a reduction in demand, output, and total savings.
B) A strong, healthy economy can be achieved if most households are heavily in debt.
C) A high savings rate will provide the funds for investment, which is a driving force of long-term economic growth.
D) A reduction in savings and an increase in consumption will expand output and employment.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following contributes to the popularity of the argument that government spending expands employment?
A) The employment generated by the additional spending is not easily seen, while the employment crowded out by taxing, spending, and borrowing is highly visible.
B) The employment generated by the additional spending is highly visible, while the employment crowded out by taxing, spending, and borrowing is largely unseen.
C) Higher taxes will be popular if they finance spending that expands employment.
D) The employment generated by the additional spending can be accomplished without increases in taxes or borrowing.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following attributes of the recession of 2008-2009 is most supportive of the Keynesian view that the crowding-out effect will be minimal during a severe recession?
A) the immediate increase in output and employment generated by the budget deficits of 2008-2009
B) the decline in the general level of prices during 2009
C) short-term interest rates falling to near zero, despite growing budget deficits during 2008-2009
D) short-term interest rates falling to near zero, as the budget deficit declined during 2008-2009
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Within the framework of the AD-AS model, an increase in savings by households will
A) increase the supply of loanable funds and reduce interest rates.
B) be offset by a decrease in savings by businesses.
C) cause long-run fluctuations in the rate of consumption.
D) result in a decline in aggregate demand, output, and employment.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 154
Related Exams