A) DNA polymerase begins adding nucleotides at the 3' end of the template.
B) Single stranded binding protein stabilizes DNA by blocking access to the 5' end.
C) Replication must progress toward the replication fork.
D) Dehydration reactions require a free -OH group.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Within a double-stranded DNA molecule, if adenine forms hydrogen bonds with thymine, and cytosine forms hydrogen bonds with guanine what consequence in the structure of the DNA?
A) It allows variable width of the double helix.
B) It permits complementary base pairing.
C) It determines the tertiary structure of a DNA molecule.
D) It determines the type of protein produced.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the enzyme topoisomerase in DNA replication?
A) relieving strain in the DNA ahead of the replication fork caused by the untwisting of the double helix
B) detecting the shape of the template base's surface to help recruit the appropriate nucleotide to pair
C) reattaching the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs in the double helix
D) building RNA primers using the parental DNA strand as a template
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are telomeres?
A) the structures that hold two sister chromatids together
B) enzymes that elongate the DNA strand during replication
C) the sites of origin of DNA replication
D) the ends of linear chromosomes
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In bacteria, which of the following proteins is responsible for removing nucleotides from the RNA primer that is used for initiation DNA synthesis?
A) Primase
B) DNA pol I
C) DNA pol III
D) DNA ligase
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The spontaneous loss of amino groups from adenine in DNA results in hypoxanthine, an uncommon base, opposite thymine. What combination of proteins could repair such damage?
A) nuclease, DNA polymerase, DNA ligase
B) telomerase, primase, DNA polymerase
C) telomerase, helicase, single-strand binding protein
D) DNA ligase, replication fork proteins, adenylyl cyclase
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to answer the following question. 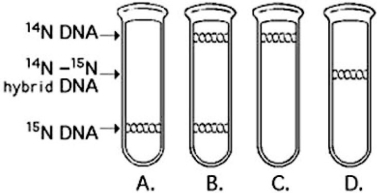 In the late 1950s, Meselson and Stahl grew bacteria in a medium containing "heavy" (radioactive) nitrogen (15N) and then transferred them to a medium containing 14N (non-radioactive) . Which of the results in the figure would be expected after one round of DNA replication in the presence of 14N?
In the late 1950s, Meselson and Stahl grew bacteria in a medium containing "heavy" (radioactive) nitrogen (15N) and then transferred them to a medium containing 14N (non-radioactive) . Which of the results in the figure would be expected after one round of DNA replication in the presence of 14N?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the structure of chromatin?
A) Heterochromatin is composed of DNA, whereas euchromatin is made of DNA and RNA.
B) Both heterochromatin and euchromatin are found in the cytoplasm.
C) Heterochromatin is highly condensed, whereas euchromatin is less compact.
D) Euchromatin is not transcribed, whereas heterochromatin is transcribed.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to answer the following question. 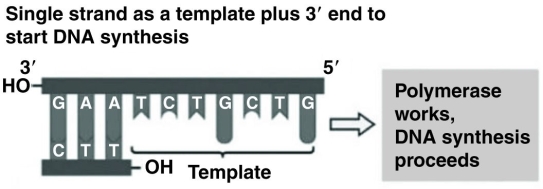 Referring to the figure, what bases will be added as DNA replication proceeds on the bottom strand?
Referring to the figure, what bases will be added as DNA replication proceeds on the bottom strand?
A) 5′ C, A, G, C, A, G, A 3′
B) 3′ T, C, T, G, C, T, G 5′
C) 5′ A, G, A, C, G, A, C 3′
D) 3′ G, T, C, G, T, C, T 5′
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In E. coli, a mutation in a gene called dnaB prevents the helicase from binding at the origin of replication. Which of the following events would you expect to occur as a result of this mutation?
A) Additional proofreading will occur.
B) No replication fork will be formed.
C) Replication will occur via RNA polymerase alone.
D) Replication will require a DNA template from another source.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a reason that the low error rate of DNA replication is important to evolution?
A) Replication with a high error rate is likely to kill the cell.
B) Fixing replication errors provides a cellular role for mismatch repair enzymes.
C) Rare errors are the source of variation.
D) Most mutations have no effect on phenotype.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A replication error results in a zygote that has inactive telomerase, which of the following characteristics would you expect to see in the organism that develops?
A) a high probability of somatic cells becoming cancerous
B) an inability to produce Okazaki fragments
C) an inability to repair thymine dimers
D) a reduction in chromosome length in gametes
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a healthy eukaryotic cell, the rate of DNA repair is typically equal to the rate of DNA mutation. Which of the following is most likely to result if the rate of repair lags behind the rate of mutation?
A) the cell can be transformed into a cancerous cell
B) RNA may be used instead of DNA as inheritance material
C) DNA replication will proceed more quickly
D) DNA replication will continue by a new mechanism
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the difference between the leading strand and the lagging strand in DNA replication?
A) The leading strand is synthesized in the 3'→ 5' direction in a discontinuous fashion, while the lagging strand is synthesized in the 5'→ 3' direction in a continuous fashion.
B) The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5'→ 3' direction, while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in the 5'→ 3' direction.
C) The leading strand requires an RNA primer, whereas the lagging strand does not.
D) There are different DNA polymerases involved in elongation of the leading strand and the lagging strand.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA is isolated from bacteria undergoing DNA replication. After heat treatment to disrupt H-bonds the DNA is centrifuged and it separates into two classes. One class of DNA includes very large molecules (thousands or even millions of nucleotides long) , and the other includes short stretches of DNA (several hundred to a few thousand nucleotides in length) . Which types of DNA do the two classes most likely represent?
A) leading strands and Okazaki fragments
B) lagging strands and Okazaki fragments
C) Okazaki fragments and Origin of replication
D) leading strands and fragments generated due to replication errors
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of double-stranded DNA contains 42% cytosine. Approximately what percent of the nucleotides in this sample will be thymine?
A) 8%
B) 16%
C) 42%
D) 58%
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Researchers found a strain of bacteria that had mutation rates one hundred times higher than normal. Which of the following statements correctly describes the most likely cause of these results?
A) The single-strand binding proteins were malfunctioning during DNA replication.
B) There were one or more base pair mismatches in the RNA primer.
C) The proofreading mechanism of DNA polymerase was not working properly.
D) The DNA polymerase was unable to add bases to the growing nucleic acid chain.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the difference between the leading and the lagging strands of DNA in DNA replication?
A) The leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction.
B) The leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end.
C) The lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched together.
D) The leading strand is synthesized at twice the rate of the lagging strand.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a nucleosome, the DNA is wrapped around ________.
A) histones
B) ribosomes
C) polymerase molecules
D) a thymine dimer
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which answer best describes the role of telomerase in replicating the ends of linear chromosomes?
A) It adds a 5' cap structure to the chromosome ends that resists degradation by nucleases.
B) It causes specific double-strand DNA breaks that result in blunt ends on both strands.
C) It catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres, compensating for the shortening that could occur during replication without telomerase activity.
D) It adds numerous GC pairs, which resist hydrolysis and maintain chromosome integrity.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 65
Related Exams