A) collusion.
B) price discrimination.
C) bulk ordering.
D) artificial competition.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In practice, oligopolistic markets are:
A) fairly common.
B) very rare.
C) forbidden by the government.
D) usually protected by the government.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do most countries handle cartels?
A) They protect cartels.
B) They have laws against firms making agreements about prices or quantities.
C) They impose strict regulations on advertising.
D) They allow cartels to exist, because it is often too difficult to regulate them.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of entry and exit into a monopolistically competitive market continues until:
A) profits are zero.
B) long run equilibrium is reached.
C) price is equal to average total cost.
D) All of these are true.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the demand curve for a firm in a monopolistically competitive market is shifting to the right, it will stop shifting when:
A) the firm raises its price.
B) the firm lowers its price.
C) firms stop entering the market.
D) firms stop exiting the market.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Large barriers to entry exist in which of the following market structures? Perfection competition Oligopoly Monopoly
A) I and II only
B) III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays the cost and revenue curves associated with a monopolistically competitive firm. 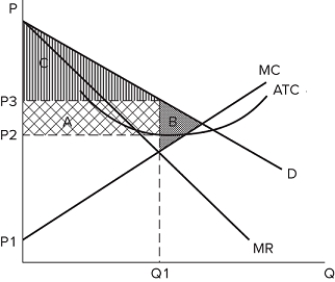 This firm will earn:
This firm will earn:
A) positive profits equal to area A.
B) positive profits equal to area C.
C) negative profits (a loss) equal to area A.
D) negative profits (a loss) equal to area B.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If we were to compare the monopolistically competitive firm's long-run outcome to that of a perfectly competitive firm, we would conclude that the monopolistically competitive firm:
A) creates less consumer surplus.
B) produces more output.
C) earns the same profit.
D) All of these are true.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a single firm in an oligopolistic market decides to increase output, that firm:
A) feels the quantity effect, but other firms feel the price effect.
B) feels both the quantity and price effects, but other firms only feel the price effect.
C) feels the price effect, but other firms feel the quantity effect.
D) feels the price effect, but other firms feel both the price and quantity effects.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price effect outweighs the quantity effect, the oligopolistic firm:
A) has an incentive to increase output.
B) has no incentive to decrease output.
C) has no incentive to increase output.
D) None of these is true.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long run economic profits are possible in which of the following market structures? Oligopoly Monopolistic competition Monopoly
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays the cost and revenue curves associated with a monopolistically competitive firm. 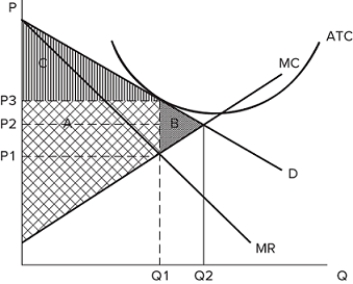 If the firm is producing Q1 and charging P3, it is likely:
If the firm is producing Q1 and charging P3, it is likely:
A) in long run equilibrium.
B) at an efficient outcome.
C) not maximizing profits.
D) operating at a loss.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is one of the defining characteristics of an oligopoly?
A) The strategic interactions between a firm and its rivals have a major impact on each firm's profits.
B) No single firm has an impact on the market as a whole.
C) There are only a few buyers in the market.
D) There are no barriers to entry to the market.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If firms in a monopolistically competitive market are earning negative economic profits, the demand curve of a single firm will likely shift to the _______ as other firms _______ the industry.
A) right; exit
B) left; exit
C) right; enter
D) left; enter
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shown displays the cost and revenue curves associated with a monopolistically competitive firm. 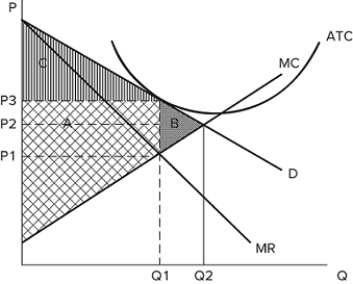 If the firm produces Q1 and charges P3, then area C represents:
If the firm produces Q1 and charges P3, then area C represents:
A) producer surplus.
B) consumer surplus.
C) deadweight loss.
D) profits.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the quantity effect outweighs the price effect, the oligopolistic firm may find it optimal to:
A) exit the industry.
B) collude.
C) increase output.
D) decrease output.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run outcome of the monopolistically competitive firm:
A) is not efficient.
B) does not maximize profits.
C) is the same as the short run outcome.
D) maximizes total surplus.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistically competitive firm can achieve product differentiation by creating:
A) a truly unique product.
B) the perception of differences in its product.
C) a product that cannot be easily substituted with a competitor's product.
D) All of these are true.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the quantity effect outweighs the price effect, firms in an oligopoly may have an incentive to:
A) increase output.
B) decrease output.
C) maintain the level of output.
D) exit the industry.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopolistically competitive firm is suffering losses in the short run, the exit of competing from the market will:
A) shift the firm's demand to the right.
B) shift the firm's demand to the left.
C) cause price to drop, but will not affect the firm's demand curve.
D) cause price to rise, but will not affect the firm's demand curve.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 157
Related Exams