A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following environments would there be the greatest need for osmoregulation?
A) an animal connective tissue cell bathed in isotonic body fluid
B) a salmon moving from a river into an ocean
C) a red blood cell surrounded by plasma
D) a plant being grown hydroponically in a watery mixture of designated nutrients
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sodium-potassium pump ________.
A) moves three potassium ions out of a cell and two sodium ions into a cell while producing ATP for each cycle
B) moves three sodium ions out of a cell and two potassium ions into a cell using energy from ATP hydrolysis
C) moves three potassium ions out of a cell and two sodium ions into a cell using energy from ATP hydrolysis
D) move three sodium ions out of a cell and two potassium ions into a cell and generates an ATP in each cycle
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes, phospholipids ________.
A) can move laterally along the plane of the membrane
B) frequently flip-flop from one side of the membrane to the other
C) occur in an uninterrupted bilayer, with membrane proteins restricted to the surface of the membrane
D) have hydrophilic tails in the interior of the membrane
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily?
A) large and hydrophobic
B) small and hydrophobic
C) large polar
D) small and ionic
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three lab groups carried out an experiment to identify the concentration of sucrose in six solutions. Each unknown contained one of the following sucrose concentrations: 0.0 M, 0.2 M, 0.4 M, 0.6 M, 0.8 M, and 1.0 M. Cubes of sweet potato (1 cm³) were soaked for 24 hours in each solution and weighed to determine the change in mass. Each data entry represents the average of three sample replicates expressed as percent change in mass following a 24-hour soak in the unknown solutions. Based on the data provided, the intracellular molarity of dissolved solutes in sweet potato cells is approximately ________.
A) 0.2 M
B) 0.4 M
C) 0.6 M
D) 0.8 M
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of molecules lack hydrophilic domains?
A) transmembrane proteins
B) integral membrane proteins
C) peripheral membrane proteins
D) cholesterol
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis is that ________.
A) pinocytosis brings only water molecules into the cell, but receptor-mediated endocytosis brings in other molecules as well
B) pinocytosis increases the surface area of the plasma membrane, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis decreases the plasma membrane surface area
C) pinocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis offers more selectivity
D) pinocytosis can concentrate substances from the extracellular fluid, but receptor-mediated endocytosis cannot
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a cell is in equilibrium with its environment, which of the following processes occurs for substances that can diffuse through the plasma membrane?
A) There is directed movement of substances into and out of the cell.
B) There is random movement of substances into and out of the cell.
C) There is no movement of substances into or out of the cell.
D) All movement of molecules across the plasma membrane occurs by active transport.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is a reasonable explanation for why unsaturated fatty acids help keep a membrane more fluid at lower temperatures?
A) The double bonds form kinks in the fatty acid tails, preventing adjacent lipids from packing tightly.
B) Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content, which prevents adjacent lipids from packing tightly.
C) Unsaturated fatty acids are more nonpolar than saturated fatty acids.
D) The double bonds block interaction among the hydrophilic head groups of the lipids.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An organism with a cell wall would most likely be unable to take in materials through ________.
A) osmosis
B) active transport
C) phagocytosis
D) facilitated diffusion
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The solutions in the arms of a U-tube are separated at the bottom of the tube by a selectively permeable membrane. The membrane is permeable to sodium chloride but not to glucose. Side A is filled with a solution of 0.4 M glucose and 0.5 M sodium chloride (NaCl) , and side B is filled with a solution containing 0.8 M glucose and 0.4 M sodium chloride. Initially, the volume in both arms is the same.
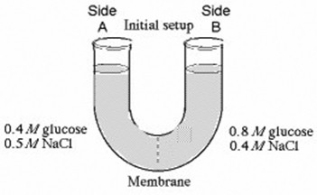 At the beginning of the U-tube experiment illustrated above, which of the following statements is true?
At the beginning of the U-tube experiment illustrated above, which of the following statements is true?
A) Side A is hypertonic to side B.
B) Side A is hypotonic to side B.
C) Side A is hypertonic to side B with respect to glucose.
D) Side A is hypotonic to side B with respect to NaCl.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An animal cell lacking carbohydrates on the external surface of its plasma membrane would likely be impaired in which function?
A) transporting ions against an electrochemical gradient
B) cell-cell recognition
C) attaching the plasma membrane to the cytoskeleton
D) establishing a diffusion barrier to charged molecules
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description.
-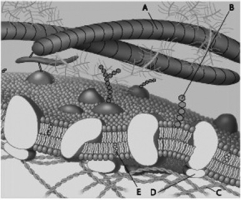 Which component in the accompanying figure is hydrophilic?
Which component in the accompanying figure is hydrophilic?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a plant cell, such as one from a tulip leaf, is submerged in a hypertonic solution, what is likely to occur?
A) The cell will burst.
B) Plasmolysis will shrink the interior of the cell.
C) The cell will become flaccid.
D) The cell will become turgid.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What will happen to a red blood cell (RBC) , which has an internal ion content of about 0.9%, if it is placed into a beaker of pure water?
A) The cell would shrink because the water in the beaker is hypotonic relative to the cytoplasm of the RBC.
B) The cell would shrink because the water in the beaker is hypertonic relative to the cytoplasm of the RBC.
C) The cell would swell because the water in the beaker is hypotonic relative to the cytoplasm of the RBC.
D) The cell will remain the same size because the solution outside the cell is isotonic.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the paragraph and accompanying figure to answer the following questions.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects cells that have both CD4 and CCR5 cell surface molecules. The viral nucleic acid molecules are enclosed in a protein capsid, and the protein capsid is itself contained inside an envelope consisting of a lipid bilayer membrane and viral glycoproteins. One hypothesis for viral entry into cells is that binding of HIV membrane glycoproteins to CD4 and CCR5 initiates fusion of the HIV membrane with the plasma membrane, releasing the viral capsid into the cytoplasm. An alternative hypothesis is that HIV gains entry into the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis, and membrane fusion occurs in the endocytotic vesicle. To test these alternative hypotheses for HIV entry, researchers labeled the lipids on the HIV membrane with a red fluorescent dye.
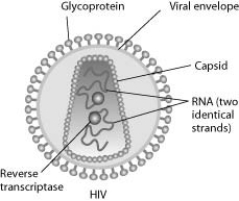 -In an HIV-infected cell producing HIV virus particles, the viral glycoprotein is expressed on the plasma membrane. How do the viral glycoproteins get to the plasma membrane? They are synthesized ________.
-In an HIV-infected cell producing HIV virus particles, the viral glycoprotein is expressed on the plasma membrane. How do the viral glycoproteins get to the plasma membrane? They are synthesized ________.
A) on ribosomes on the plasma membrane
B) by ribosomes in the rough ER and arrive at the plasma membrane in the membrane of secretory vesicles
C) on free cytoplasmic ribosomes and then inserted into the plasma membrane
D) by ribosomes in the rough ER, secreted from the cell, and inserted into the plasma membrane from the outside
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following membrane activities requires energy from ATP hydrolysis?
A) facilitated diffusion of chloride ions across the membrane through a chloride channel
B) movement of Na⁺ ions from a lower concentration in a mammalian cell to a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid
C) movement of glucose molecules into a bacterial cell from a medium containing a higher concentration of glucose than inside the cell
D) movement of carbon dioxide out of a paramecium
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Celery stalks that are immersed in fresh water for several hours become stiff. Similar stalks left in a 0.15 M salt solution become limp. From this we can deduce that the fresh water ________.
A) and the salt solution are both hypertonic to the cells of the celery stalks
B) is hypotonic and the salt solution is hypertonic to the cells of the celery stalks
C) is hypertonic and the salt solution is hypotonic to the cells of the celery stalks
D) is isotonic and the salt solution is hypertonic to the cells of the celery stalks
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is most likely true of a protein that cotransports glucose and sodium ions into the intestinal cells of an animal?
A) Sodium and glucose compete for the same binding site in the cotransporter.
B) Glucose entering the cell down its concentration gradient provides energy for uptake of sodium ions against the electrochemical gradient.
C) Sodium ions can move down their electrochemical gradient through the cotransporter whether or not glucose is present outside the cell.
D) A substance that blocks sodium ions from binding to the cotransport protein will also block the transport of glucose.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 68
Related Exams