B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Corrective taxes differ from most taxes in that corrective taxes
A) reduce economic efficiency.
B) do not raise revenue for the government.
C) do not cause deadweight losses.
D) always result in a high burden on sellers of goods to which the corrective tax applies.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A corrective tax
A) allocates pollution to those factories that face the highest cost of reducing it.
B) is a form of regulation.
C) works well for all types of externalities.
D) is inferior to regulatory policy according to most economists.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-20. 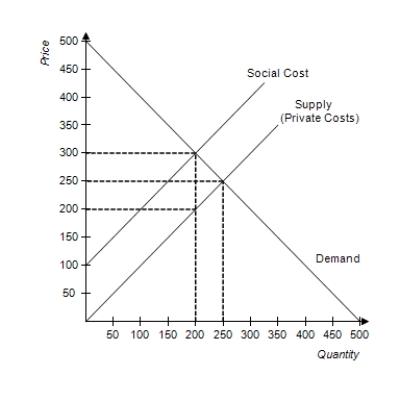 -Refer to Figure 10-20. The graph depicts the market for fertilizer. What is the socially optimal price of fertilizer?
-Refer to Figure 10-20. The graph depicts the market for fertilizer. What is the socially optimal price of fertilizer?
A) $100
B) $200
C) $250
D) $300
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that cigarette smokers create a negative externality. Further suppose that the government imposes a tax on cigarettes equal to the per-unit externality. What is the relationship between the after-tax equilibrium quantity and the socially optimal quantity of cigarettes?
A) They are equal.
B) The after-tax equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity.
C) The after-tax equilibrium quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The concept of external cost is associated with a negative externality, but not with a positive externality.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Gasoline taxes are an example of an EPA regulation.
B) Gasoline taxes are higher in many European countries than in the United States.
C) Gasoline taxes contribute to global warming.
D) Gasoline taxes are an example of a command-and-control policy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most economists prefer regulation to taxation because regulation corrects market inefficiencies at a lower cost than taxation does.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With a corrective tax, the supply curve for pollution is
A) vertical.
B) horizontal.
C) upward-sloping.
D) downward-sloping.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In some parts of the United States, sugar beets are grown and harvested. The process of producing usable sugar from the beets generates foul-smelling smoke. A government policy that limits the emission of smoke by sugar-beet-processing firms is an example of
A) a market-based policy.
B) a command-and-control policy.
C) tradable pollution permits.
D) transaction costs.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply curve for a product reflects the
A) willingness to pay of the marginal buyer.
B) quantity buyers will ultimately purchase of the product.
C) cost to sellers of producing the product.
D) seller's profit from producing the product.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 10-1 The demand curve for gasoline slopes downward and the supply curve for gasoline slopes upward. The production of the 1,000th gallon of gasoline entails the following: • a private cost of $3.10; • a social cost of $3.55; • a value to consumers of $3.70. -Refer to Scenario 10-1. From the given information, it is apparent that
A) the production of gasoline involves a negative externality, so the market will produce a smaller quantity of gasoline than is socially desirable.
B) the production of gasoline involves a negative externality, so the market will produce a larger quantity of gasoline than is socially desirable.
C) the production of gasoline involves a positive externality, so the market will produce a smaller quantity of gasoline than is socially desirable.
D) the production of gasoline involves a positive externality, so the market will produce a larger quantity of gasoline than is socially desirable.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Golden Rule is an example of a private solution for
A) subsidizing higher education.
B) internalizing externalities.
C) increasing production.
D) reducing scarcity.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a sawmill creates too much noise for local residents,
A) noise restrictions will force residents to move out of the area.
B) a sense of social responsibility will cause owners of the mill to reduce noise levels.
C) the government can raise economic well-being through noise-control regulations.
D) the government should avoid intervening because the market will allocate resources efficiently.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-18. The graph represents a corrective tax to reduce pollution. On the axes, Q denotes the quantity of pollution and P represents the price of pollution. 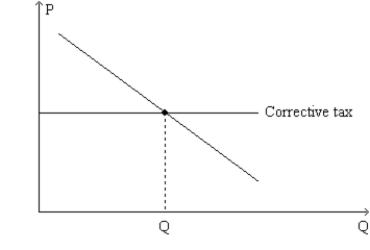 -Refer to Figure 10-18. The line labeled "Corrective tax" could accurately be re-labeled as
-Refer to Figure 10-18. The line labeled "Corrective tax" could accurately be re-labeled as
A) "Demand for clean air."
B) "Demand for pollution rights."
C) "Price of pollution."
D) "Rate of subsidy."
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose a certain good provides an external benefit. If the private cost of the last unit of the good that was produced is equal to the social value of that unit, then the sum of producer and consumer surplus is maximized.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-9 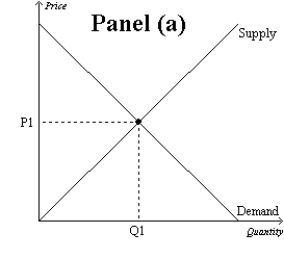
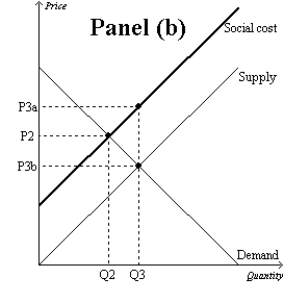
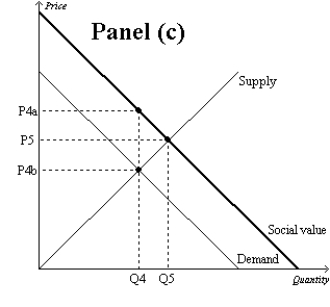 -Refer to Figure 10-9. Which graph represents a market with no externality?
-Refer to Figure 10-9. Which graph represents a market with no externality?
A) Panel (a)
B) Panel (b)
C) Panel (c)
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Although regulation and corrective taxes are both capable of reducing pollution, regulation accomplishes this goal more efficiently.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-17 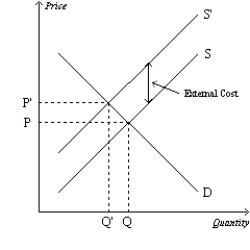 -Refer to Figure 10-17. How large would a corrective tax need to be to move this market from the equilibrium outcome to the socially-optimal outcome?
-Refer to Figure 10-17. How large would a corrective tax need to be to move this market from the equilibrium outcome to the socially-optimal outcome?
A) An amount equal to P' minus P.
B) An amount equal to P'.
C) An amount equal to P.
D) An amount equal to the external cost.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This figure reflects the market for outdoor concerts in a public park surrounded by residential neighborhoods.
Figure 10-3 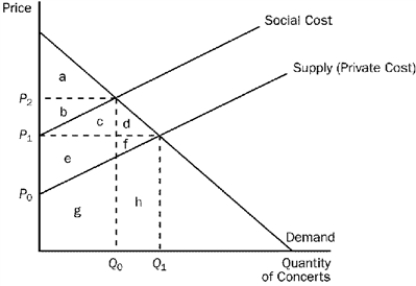 -Refer to Figure 10-3. What price and quantity combination best represents the optimum price and number of concerts that should be organized?
-Refer to Figure 10-3. What price and quantity combination best represents the optimum price and number of concerts that should be organized?
A) P1, Q1
B) P2, Q0
C) P2, Q1
D) The optimum quantity is zero concerts as long as residents in surrounding neighborhoods are adversely affected by noise and congestion.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 543
Related Exams