Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Gas exchange between the air and the blood takes place in the __________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the nasal conchae?
A) increases turbulence in the airflow
B) olfaction
C) increases surface area for cleaning, warming, and moisturizing the air
D) increases turbulence and surface area for cleaning, warming and moisturizing the air
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules acts as a buffer during the chloride shift?
A) carbon dioxide
B) hemoglobin
C) carbonic anhydrase
D) water
E) bicarbonate ion
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a passageway for both air and food?
A) trachea
B) larynx
C) pharynx
D) bronchus
E) esophagus
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a function of the respiratory system?
A) olfaction
B) taste
C) production of chemical mediators
D) voice production
E) regulation of blood pH
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whose law explains why a gas will move from one area to another area?
A) Dalton's Law
B) Henry's Law
C) Charles Law
D) Boyle's Law
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The chemosensitive area of the brain is located in the
A) pons.
B) cerebral peduncles.
C) cerebellum.
D) hypothalamus.
E) medulla oblongata.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During inspiration, contraction of the diaphragm causes the volume of Mr. Jones' thoracic cavity to increase and the pleural pressure to decrease. The pressure in his alveoli (Palv) will
A) decrease below atmospheric pressure (PB) , causing air to move out of his lungs.
B) become greater than atmospheric pressure (PB) , causing air to move into his lungs.
C) decrease below atmospheric pressure (PB) , causing air to move into his lungs.
D) become greater than atmospheric pressure (PB) , causing air to move out of his lungs.
E) does not change.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Oxygen diffusion from the alveolus to the pulmonary capillary occurs because
A) alveolar PO2 is greater than capillary PO2.
B) oxygen diffuses faster than carbon dioxide.
C) alveolar PCO2 is greater than capillary PCO2.
D) alveolar PO2 is less than capillary PCO2.
E) carbon dioxide diffuses faster than oxygen.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with the appropriate description or definition. -tidal volume "Enter the letter of the correct description below"
A) sum of the inspiratory reserve, expiratory reserve, tidal, and residual volumes
B) volume of air inspired during a normal inspiration
C) volume of air remaining in lungs after the most forceful expiration
D) sum of the expiratory reserve, inspiratory reserve, and tidal volumes
E) the amount of air that can be forcefully expired after expiration of the normal tidal volume
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
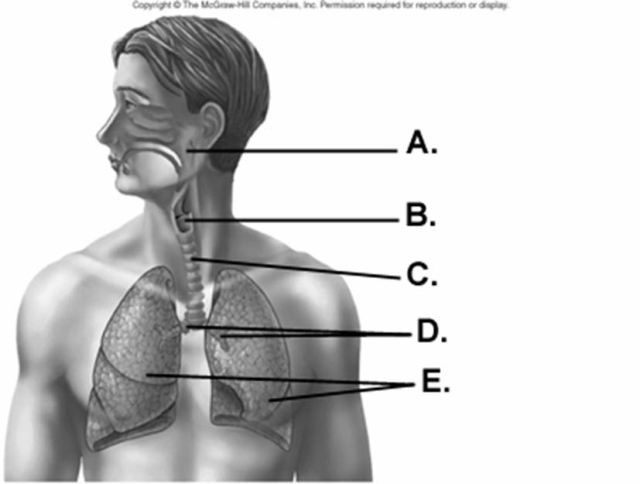 -What does "A" represent on the diagram?
-What does "A" represent on the diagram?
A) larynx
B) lungs
C) trachea
D) pharynx
E) bronchi
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The highest level of exercise that can be performed without causing a significant change in blood pH is called the
A) Hering-Breuer reflex.
B) aerobic threshold.
C) anaerobic threshold.
D) lactic acid tolerance level.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -What does "B" represent on the diagram?
-What does "B" represent on the diagram?
A) larynx
B) lungs
C) trachea
D) pharynx
E) bronchi
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When these ligaments or folds come together, they prevent food from entering the lower respiratory tract.
A) vocal folds
B) vestibular folds
C) cricothyroid ligaments
D) epiglottic folds
E) vocal folds and vestibular folds
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -What does "E" represent on the diagram?
-What does "E" represent on the diagram?
A) larynx
B) lungs
C) trachea
D) pharynx
E) bronchi
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whenever people cry, their nose runs. This is because the _____ drain tears into the nose.
A) nasolacrimal ducts
B) paranasal sinuses
C) lacrimal glands
D) Wharten's ducts
E) auditory tube
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pontine respiratory neurons
A) are located in the medulla oblongata in the brain.
B) are active only during inspiration.
C) are active only during expiration.
D) play a role in switching between inspiration and expiration.
E) is essential for respiratory rhythm.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding the lungs is correct?
A) The left lung is larger than the right lung.
B) The left lung contains two lobes while the right lung contains three lobes.
C) The left lung has more bronchopulmonary segments than the right lung.
D) Only the right lung has a hilum.
E) The left lung contains three lobes while the right lung contains two lobes.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is fetal hemoglobin very efficient at picking up oxygen?
A) The BPG levels are much higher than in maternal hemoglobin.
B) The fetal oxygen-dissociation curve is to the right of the maternal oxygen-dissociation curve.
C) The concentration of fetal hemoglobin is 10% greater than the concentration of maternal hemoglobin.
D) The fetal oxygen-dissociation curve is to the left of the maternal oxygen-dissociation curve.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 178
Related Exams